Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Hypothyroidism, commonly known as an underactive thyroid, is a health condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones to regulate the body’s metabolism. This disorder affects millions of people worldwide, including many in Nigeria, but often goes undiagnosed because its symptoms can mimic other health issues.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes of hypothyroidism in Nigeria, its symptoms, and the best treatment options available to manage the condition effectively.
What is Hypothyroidism?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It plays a vital role in controlling metabolism, body temperature, energy levels, and overall growth. When the gland underproduces thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), the body slows down, leading to several physical and emotional symptoms.
Hypothyroidism is more common in women, especially those over 35, but men and even children can also develop the condition.
Causes of underactive thyroid in Nigeria
Several factors can lead to an underactive thyroid. The most common causes of underactive thyroid in Nigeria include:
-
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis (Autoimmune Disorder):
The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks thyroid cells, reducing their ability to produce hormones. -
Iodine Deficiency:
In Nigeria, iodine deficiency remains one of the leading causes of hypothyroidism, especially in rural areas where iodized salt is not consistently used. -
Certain Medications:
Drugs such as lithium (used for mental health conditions) and amiodarone (for heart problems) can interfere with thyroid hormone production. -
Thyroid Surgery or Radiation Therapy:
Surgical removal of the thyroid or treatments for thyroid cancer and hyperthyroidism may result in hypothyroidism. -
Congenital Hypothyroidism:
Some babies are born with an underactive thyroid, highlighting the importance of newborn screening.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
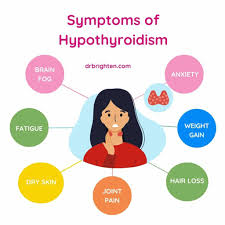
Hypothyroidism develops gradually, and its symptoms can be subtle at first. However, as hormone levels continue to drop, symptoms become more noticeable. Common hypothyroidism symptoms in women and men include:
-
Persistent fatigue and low energy
-
Weight gain despite no changes in diet or exercise
-
Cold intolerance (feeling unusually cold)
-
Constipation and sluggish digestion
-
Dry skin, brittle nails, and hair loss
-
Depression, forgetfulness, or low mood
-
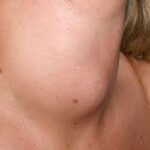
Puffy face and swollen neck
-
Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
-
Hoarseness of voice
In women, under active thyroid may also cause irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and complications during pregnancy if left untreated.
How underactive thyroid is Diagnosed
A proper diagnosis requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
-
Blood Tests:
-
TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone): High TSH levels often indicate hypothyroidism.
-
Free T4: Measures the actual thyroid hormone circulating in the blood.
-
Doctors may also perform ultrasound scans to check for thyroid nodules or enlargement.
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
The good news is that underactive thyroid is a treatable condition, and most patients live normal lives with the right care.
-
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy:
-
The most common treatment is Levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4 hormone.
-
It is taken daily as a pill to restore hormone levels.
-
Patients must take it consistently and undergo regular blood tests to adjust dosage.
-
-
Lifestyle Support and Home Care:
-
Balanced Diet: Eat iodine-rich foods (fish, eggs, dairy, and iodized salt) but avoid excessive intake of goitrogenic foods (like raw cabbage, soy, and cassava).
-
Regular Exercise: Helps maintain weight and energy levels.
-
Mental Health Care: Counseling or support groups can help manage depression or mood changes.
-
Routine Check-ups: Continuous monitoring ensures proper hormone balance.
-
Can Hypothyroidism Be Prevented?
While autoimmune causes cannot be prevented, iodine deficiency-related hypothyroidism can be reduced by using iodized salt and ensuring proper nutrition. Pregnant women should also have their thyroid function checked, as untreated hypothyroidism can harm both mother and baby.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a growing health concern in Nigeria, often linked to iodine deficiency, autoimmune disease, and lifestyle factors. Early detection and proper treatment with thyroid hormone replacement therapy allow patients to live healthy, productive lives.
If you experience persistent fatigue, weight changes, or unexplained mood swings, it may be time to ask your doctor about thyroid testing.
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem