Common Thyroid Disorders Explained

The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, but despite its size, it plays a major role in regulating metabolism, growth, and overall health. When the thyroid doesn’t function properly, it can lead to a range of disorders that impact energy levels, weight, mood, heart health, and more.
In this article, we will break down the most common thyroid disorders—including hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer—their symptoms, causes, and available treatments.
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
Common Causes
-
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (an autoimmune condition)
-
Iodine deficiency
-
Certain medications (e.g., lithium)
-
Previous thyroid surgery or radiation
Symptoms
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Weight gain (despite no change in diet)
-
Dry skin and brittle hair
-
Constipation
-
Sensitivity to cold
-
Depression or low mood
Treatment
Hypothyroidism is usually managed with thyroid hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine), which restores normal hormone levels and relieves symptoms.
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, speeding up metabolism.
Common Causes
-
Graves’ disease (autoimmune condition)
-
Toxic multinodular goiter
-
Thyroid nodules that overproduce hormones
-
Excessive iodine intake
Symptoms
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Increased appetite
-
Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
-
Anxiety, irritability, and nervousness
-
Excessive sweating
-
Difficulty sleeping
-
Bulging eyes (in Graves’ disease)
Treatment
Options include:
-
Anti-thyroid medications (methimazole, propylthiouracil)
-
Radioactive iodine therapy to shrink the gland
-
Surgery (thyroidectomy) in severe cases
3. Goiter (Enlarged Thyroid Gland)
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. It can be associated with both underactive or overactive thyroid function, or sometimes normal thyroid levels.
Causes
-
Iodine deficiency (common in regions with low iodine in diets)
-
Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease
-
Thyroid nodules
-
Pregnancy (hormonal changes can enlarge the thyroid)
Symptoms
-
Visible swelling in the neck
-
Tightness in the throat
-
Difficulty swallowing or breathing (in large goiters)
Treatment
-
Iodine supplementation (if deficiency-related)
-
Medication for underlying thyroid disease
-
Surgery in severe cases causing compression
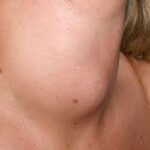
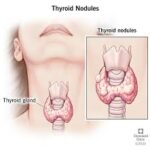
4. Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are lumps that form within the thyroid gland. Most are benign (non-cancerous), but some may be malignant.
Causes
-
Iodine deficiency
-
Overgrowth of thyroid tissue
-
Cysts filled with fluid
-
Thyroid cancer (in rare cases)
Symptoms
-
Often no symptoms (discovered during routine checkups)
-
Lump or swelling in the neck
-
Hoarseness or voice changes
-
Difficulty swallowing
Diagnosis
-
Ultrasound to assess size and shape
-
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy to rule out cancer
Treatment
-
Regular monitoring for small, benign nodules
-
Surgery or radioactive iodine for suspicious or large nodules
5. Thyroid Cancer
Although relatively rare, thyroid cancer is one of the most serious thyroid conditions. It occurs when abnormal thyroid cells grow uncontrollably.
Risk Factors
-
Family history of thyroid cancer
-
Radiation exposure to the neck
-
Female gender (higher risk than men)
-
Certain genetic conditions
Symptoms
-
Lump in the neck that doesn’t go away
-
Persistent hoarseness
-
Difficulty swallowing or breathing
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Treatment
-
Surgery (thyroidectomy)
-
Radioactive iodine therapy
-
Thyroid hormone therapy (to suppress recurrence)
-
Targeted therapy or chemotherapy (in advanced cases)
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are common, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, most people can lead healthy lives.
-
Hypothyroidism slows metabolism but is easily managed with hormone replacement.
-
Hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolism and can be controlled with medication or surgery.
-
Goiter and thyroid nodules often require careful monitoring.
-
Thyroid cancer, though rare, can be effectively treated if caught early.
If you notice persistent fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, or a lump in your neck, consult a healthcare provider. Regular checkups and thyroid function tests are essential for early detection and treatment.
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem