Goiter: Why the Neck Swells and How it’s Treated
Goiter is one of the most common thyroid conditions worldwide and remains a major public health concern in Nigeria. It refers to the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck. While not every goiter is serious, it can sometimes indicate an underlying thyroid disorder that requires medical attention.
In Nigeria, where iodine deficiency is still a challenge in certain rural areas, goiter continues to affect thousands of people. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of goiter is essential for early detection and better health outcomes.
What is Goiter?
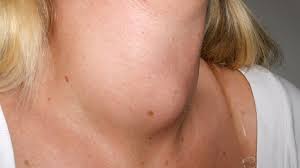
Goiter is simply the swelling of the thyroid gland, which may present as a noticeable lump in the front of the neck. The thyroid plays a key role in regulating metabolism, growth, and hormone balance. When it becomes enlarged, it could mean the thyroid is either underactive (hypothyroidism), overactive (hyperthyroidism), or functioning normally despite its size.
Causes of Goiter
Several factors can lead to thyroid enlargement:
-
Iodine Deficiency
-
The most common cause of goiter worldwide.
-
The thyroid needs iodine to produce hormones. When the diet lacks sufficient iodine (common in areas without iodized salt), the gland enlarges in an attempt to compensate.
-
In Nigeria, iodine deficiency remains a leading cause of endemic goiter, particularly in rural communities.
-
-
Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
-
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (underactive thyroid) and Graves’ disease (overactive thyroid) can both cause goiter.
-
-
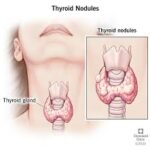
Thyroid Nodules
-
Small lumps (benign or malignant) may form within the thyroid and lead to visible swelling.
-
-
Other Factors
-
Hormonal changes (especially in women), genetic predisposition, and excessive or deficient iodine intake.
-
Symptoms of Goiter
The most obvious sign is a visible swelling in the neck, but other symptoms may include:
-
Tightness in the throat
-
Hoarseness of voice
-
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
-
Breathing difficulties (if the swelling presses on the airway)
-
Signs of thyroid dysfunction (fatigue, weight changes, rapid heartbeat, or mood swings) depending on whether the thyroid is underactive or overactive
In many cases, small goiters cause no symptoms and are only discovered during a routine medical exam.
Diagnosis of Goiter
Doctors use several methods to diagnose it such as:
-
Physical examination of the neck
-
Blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4)
-
Ultrasound scan to check for nodules and the size of the gland
-
Fine needle aspiration biopsy if cancer is suspected
Treatment options
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, severity, and symptoms:
-
Iodine Supplementation
-
For goiters caused by iodine deficiency, adding iodine-rich foods (fish, seaweed, dairy, iodized salt) can help.
-
Public health programs promoting iodized salt use in Nigeria have reduced cases, but challenges remain in remote areas.
-
-
Medications
-
Levothyroxine for underactive thyroid.
-
Antithyroid drugs for overactive thyroid (e.g., methimazole, propylthiouracil).
-
-
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
-
Used in hyperthyroidism to shrink the thyroid gland.
-
-
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
-
Recommended for very large goiters causing breathing/swallowing problems, or if there is suspicion of thyroid cancer.
-
Preventing Goiter in Nigeria
-
Use iodized salt consistently in cooking.
-
Eat iodine-rich foods (seafood, eggs, dairy).
-
Regular thyroid check-ups, especially for women (who are more prone to thyroid issues).
-
Public health campaigns to ensure awareness in communities where goiter is still common.
Key Takeaways
-
Goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, often linked to iodine deficiency, autoimmune thyroid diseases, or nodules.
-
Symptoms range from a simple neck swelling to difficulty breathing or swallowing in severe cases.
-
Goiter treatment in Nigeria depends on the cause, from iodine supplementation to surgery.
-
Preventing goiter starts with iodized salt use and early medical intervention.
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem