Hyperthyroidism: Understanding Overactive Thyroid

Hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid, is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too many hormones. This small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck controls metabolism, heart rate, digestion, and energy use. When it becomes overactive, the body works in “overdrive,” leading to several serious health challenges.
In Nigeria and globally, hyperthyroidism is often underdiagnosed because its symptoms—such as anxiety, sweating, or weight loss—can be mistaken for other conditions. However, if left untreated, it can cause dangerous complications, including heart problems and thyroid storm.
What Causes Hyperthyroidism?
Several factors can trigger an overactive thyroid, including:
-
Graves’ Disease – An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid, causing it to produce too many hormones.
-
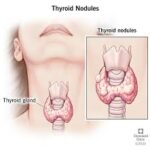
Thyroid Nodules – Lumps in the thyroid that produce hormones independently of the gland’s normal regulation.
-
Excessive Iodine Intake – Consuming too much iodine from diet, supplements, or medications can overstimulate the thyroid.
-
Thyroid Inflammation (Thyroiditis) – Sometimes the gland becomes inflamed, releasing stored hormones into the bloodstream.
-
Medications – Certain drugs, like amiodarone (used for heart rhythm disorders), can cause hyperthyroidism.
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Because thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, too much of them speeds up body processes. Key symptoms include:
-
Unexplained weight loss despite normal or increased appetite
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
-
Increased sweating and heat intolerance
-
Nervousness, irritability, and anxiety
-
Tremors in the hands or fingers
-
Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
-
More frequent bowel movements
-
Thinning hair and fragile skin
In women, hyperthyroidism may also cause irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, or complications during pregnancy.
Possible Complications of Overactive thyroid
If untreated, an overactive thyroid can lead to severe health issues, such as:
-
Thyroid Storm – A life-threatening condition with dangerously high hormone levels, causing fever, confusion, and rapid heartbeat.
-
Heart Problems – Increased risk of atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions.
-
Bone Weakness (Osteoporosis) – Excess hormones can weaken bones over time.
-
Eye Problems (Graves’ Ophthalmopathy) – Bulging eyes, irritation, and vision problems in patients with Graves’ disease.
How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to confirm overactive thyroid, including:
-
Blood Tests – Checking thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), T3, and T4 hormone levels.
-
Thyroid Scan – To check if nodules are present and whether they are overactive.
-
Ultrasound – To look for enlargement or growths in the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cause, severity, and patient’s overall health. Common approaches include:
-
Antithyroid Medications
-
Drugs like methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU) reduce hormone production.
-
Often the first treatment option in Nigeria and globally.
-
-
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
-
Radioactive iodine is swallowed to destroy overactive thyroid cells.
-
Used when medications are not effective or relapse occurs.
-
-
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
-
In severe cases or when nodules are large, part or all of the thyroid may be removed.
-
Patients will need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement afterward.
-
-
Lifestyle Support
-
Eating a balanced diet with controlled iodine intake.
-
Managing stress, regular medical check-ups, and limiting caffeine.
-
Managing Hyperthyroidism in Nigeria
In Nigeria, access to early diagnosis and treatment is key to preventing complications. Unfortunately, many patients present late due to lack of awareness. Increasing education about overactive thyroid symptoms can save lives.
If you experience unexplained weight loss, rapid heartbeat, or constant anxiety, it is important to see a healthcare professional for testing.
Conclusion
Hyperthyroidism is a serious but manageable condition. With proper diagnosis, medication, or treatment, patients can live healthy and normal lives. Raising awareness about causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial to reducing the burden of thyroid disease in Nigeria.
If you suspect you might have an overactive thyroid, don’t ignore the signs—early detection is the key to effective treatment and long-term wellness.
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem