Thyroid Cancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment
Thyroid cancer, although rare compared to other cancers, is one of the most serious thyroid disorders. It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the thyroid gland—a small, butterfly-shaped organ in the front of the neck that regulates metabolism, growth, and energy levels.
In recent years, awareness about this cancer in Nigeria has grown, yet many people still struggle with late diagnosis due to lack of routine screening and poor knowledge about its symptoms. Understanding the risk factors, early warning signs, and available treatments is essential for better outcomes.
Risk Factors for Thyroid Cancer
While the exact cause is unknown, certain factors increase the likelihood of developing this cancer:
-
Family history of thyroid cancer – Genetics play a strong role, especially if close relatives have had thyroid cancer.
-
Radiation exposure to the neck – Previous radiation therapy in childhood or adolescence increases risk.
-
Gender and age – Women are three times more likely to develop thyroid cancer than men. It is most common between ages 30–50.
-
Genetic conditions – Certain inherited syndromes (e.g., multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2) can predispose individuals.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer often develops slowly and may not cause early symptoms. However, as it progresses, signs may include:
-
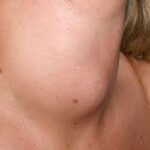
A lump in the neck that doesn’t go away.
-
Persistent hoarseness or voice changes.
-
Difficulty swallowing or breathing if the tumor presses on the windpipe or esophagus.
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
👉 If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor for evaluation.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several tests to confirm thyroid cancer:
-
Physical exam to check for lumps.
-
Ultrasound to evaluate the thyroid and surrounding lymph nodes.
-
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) to check for cancer cells.
-
Blood tests (TSH, T3, T4) to assess thyroid function.
-
CT scans or MRI for advanced cases.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and stage of thyroid cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health:
-
Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
-
The most common treatment is partial or total removal of the thyroid gland.
-
-
Radioactive Iodine Therapy (RAI)
-
Used after surgery to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
-
-
Thyroid Hormone Therapy
-
Patients take daily levothyroxine to replace missing thyroid hormones and suppress TSH (which can stimulate cancer growth).
-
-
Targeted Therapy or Chemotherapy
-
Used in advanced or aggressive cases that do not respond to surgery or RAI.
-
Living with Thyroid Cancer
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, most patients live long and healthy lives. Regular follow-up with an endocrinologist or oncologist is essential. Patients may need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, along with routine scans and blood tests.
Written by Fawzi Rufai, Medically Reviewed by Sesan Kareem