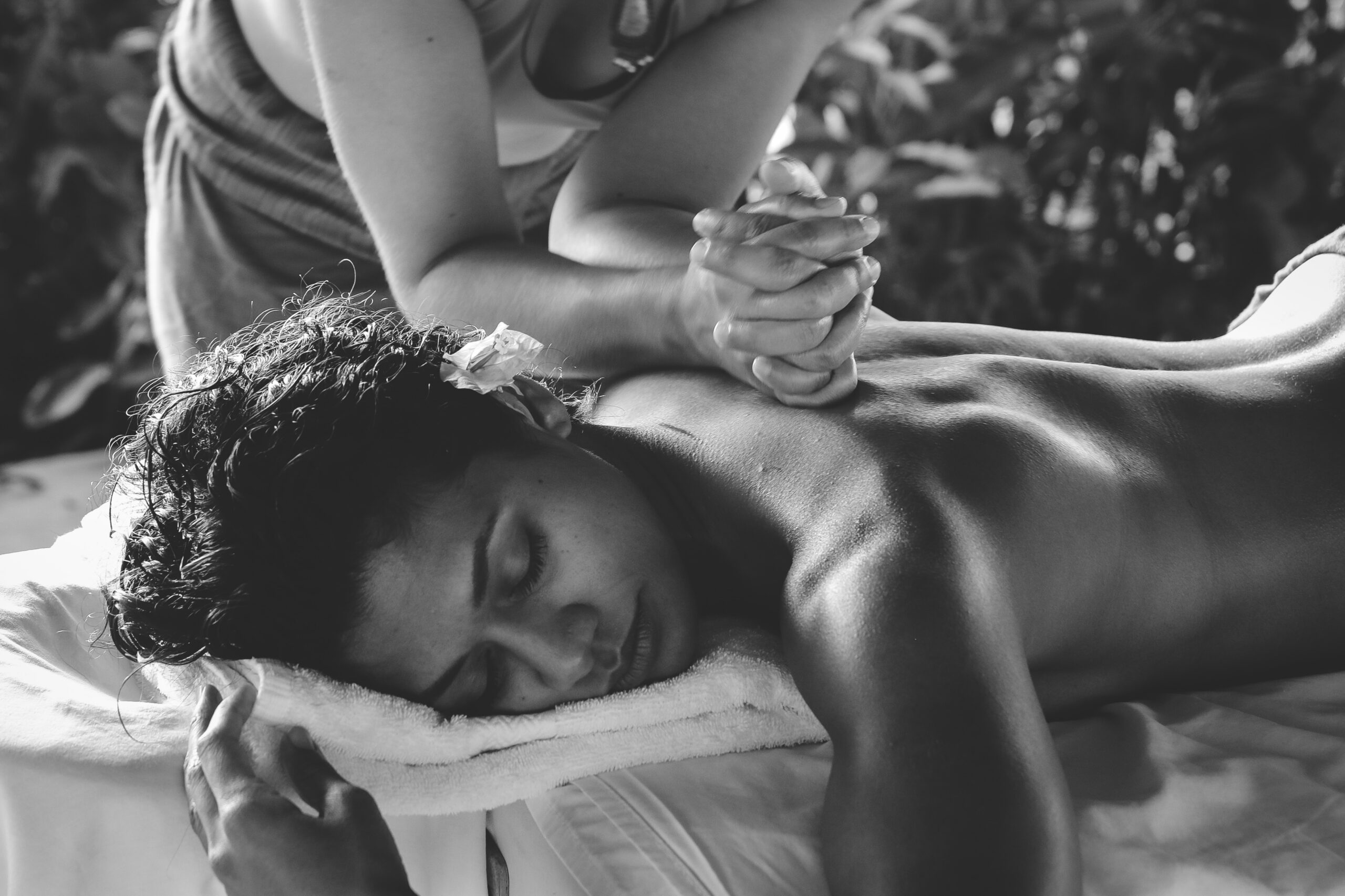
Chronic Pain Management in African Women: A Comprehensive Approach to Well-being

Chronic pain, characterized by persistent discomfort lasting for more than three to six months, is a global health challenge that affects millions of individuals.

Chronic Pain Management in African Women
In the context of Africa, chronic pain poses unique considerations, and its impact on women is particularly noteworthy. Exploring the multifaceted aspects of chronic pain management in African women requires a comprehensive understanding of cultural, socio-economic, and healthcare system dynamics.
Understanding the Burden of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain affects African women across diverse demographics, but its prevalence is often underestimated. Factors such as cultural stigma around discussing pain, limited access to healthcare resources, and disparities in pain management contribute to the silent suffering of many women. Common conditions leading to chronic pain in African women include musculoskeletal disorders, sickle cell disease, neuropathic pain, and gynecological issues.
Common Types of Pain Experience By African Women
African women, like women globally, experience a range of common types of pain, which can be influenced by cultural, socio-economic, and healthcare factors. Here are some of the common types of pain experienced by African women:
- Musculoskeletal Pain:
- Causes: Musculoskeletal pain can result from various factors, including physical strain, poor ergonomics, or underlying conditions such as arthritis.
- Prevalence: Many African women engage in physically demanding activities, such as agricultural work or manual labor, which can contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
- Gynecological Pain:
- Causes: Conditions like endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), uterine fibroids, and menstrual cramps can cause chronic gynecological pain.
- Prevalence: Gynecological conditions are prevalent among African women, and limited access to gynecological healthcare may lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Neuropathic Pain:
- Causes: Diseases like diabetes, infections, or injuries can lead to neuropathic pain, characterized by tingling, burning, or shooting sensations.
- Prevalence: Diabetes, in particular, is a growing health concern in Africa, contributing to an increase in neuropathic pain cases among women.
- Sickle Cell Disease Pain:
- Causes: Sickle cell disease, a genetic disorder, can cause acute and chronic pain episodes known as vaso-occlusive crises.
- Prevalence: Sickle cell disease is more prevalent in populations with African ancestry, and women with the condition often experience recurrent pain episodes.
- Headaches and Migraines:
- Causes: Stress, hormonal changes, and environmental factors can trigger headaches and migraines.
- Prevalence: Headaches and migraines are common worldwide, but they may be exacerbated by factors such as stress or lack of access to consistent healthcare.
- Trauma-Related Pain:
- Causes: Trauma, including physical injuries or accidents, can lead to acute or chronic pain.
- Prevalence: In regions facing conflicts or high levels of violence, women may be more susceptible to trauma-related pain.
- Post-Surgical Pain:
- Causes: After surgical procedures, women may experience post-surgical pain during the recovery period.
- Prevalence: Access to safe and timely surgical interventions can vary, affecting the prevalence of post-surgical pain experiences.
- Psychosomatic Pain:
- Causes: Emotional and psychological factors can contribute to psychosomatic pain, which is pain experienced in the absence of clear physical pathology.
- Prevalence: Sociocultural factors, stigma, and limited access to mental health services may contribute to the prevalence of psychosomatic pain.
Factors Influencing Pain Experiences in African Women:
- Cultural Beliefs and Practices:
- Cultural norms may influence how pain is perceived and expressed, impacting the likelihood of seeking medical help.
- Socio-Economic Factors:
- Limited access to healthcare resources, including pain management specialists, may contribute to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Reproductive Health Factors:
- Gynecological conditions and reproductive health issues, prevalent among women, contribute significantly to pain experiences.
- Infectious Diseases:
- Diseases like HIV/AIDS, prevalent in some African regions, can cause pain as a symptom or a result of related complications.
- Environmental and Occupational Factors:
- Engaging in physically demanding activities or exposure to environmental factors may contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
- Access to Healthcare:
- Limited access to healthcare, particularly in rural areas, may result in unmanaged or undermanaged pain conditions.
Understanding the specific types of pain experienced by African women is crucial for developing targeted healthcare strategies that address the unique challenges faced by this demographic. A holistic approach that considers cultural, socio-economic, and healthcare system factors is essential for effective pain management and improving the overall well-being of African women.
Medical Interventions:
- Pharmacotherapy:
- Analgesics: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications can help manage chronic pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and opioids are commonly prescribed based on the severity and type of pain.
- Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants: Certain medications traditionally used to treat depression or seizures have proven effective in managing chronic pain conditions.
- Injections:
- Nerve Blocks: Injections targeting specific nerves or nerve groups can provide temporary relief for chronic pain, especially in cases of neuropathic pain.
- Corticosteroids: Injections of corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in affected joints or areas.
- Surgical Interventions:
- In some cases, surgical procedures may be recommended to address the root cause of chronic pain, such as herniated discs or joint abnormalities.
Physical and Rehabilitation Therapies:
- Physical Therapy:
- Tailored exercise programs and physical therapy sessions can improve flexibility, strength, and mobility, reducing the impact of chronic pain on daily life.
- Occupational Therapy:
- Occupational therapists work with individuals to develop strategies for managing pain during daily activities, ensuring maximum functionality.
- Mind-Body Therapies:
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Mindful movement practices can enhance physical well-being and provide relaxation, contributing to pain management.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: These techniques help individuals cultivate a heightened awareness of their bodies, fostering better pain coping mechanisms.
Psychological and Behavioral Approaches:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
- CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with chronic pain, promoting a more positive mindset.
- Biofeedback:
- This technique involves monitoring physiological functions (e.g., muscle tension, heart rate) and learning to control them to reduce pain.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture:
- Traditional Chinese medicine, such as acupuncture, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Herbal Remedies:
- Certain herbs, such as turmeric and ginger, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and may contribute to pain management.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Exercise and Physical Activity:
- Engaging in regular, low-impact exercises can help maintain joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve overall well-being.
- Healthy Diet:
- A well-balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may contribute to reducing pain and inflammation.
- Sleep Hygiene:
- Establishing healthy sleep patterns is crucial, as adequate rest promotes healing and resilience to pain.
Cultural Perspectives on Pain
Cultural attitudes toward pain influence the expression and management of chronic pain. In many African communities, there exists a stoic acceptance of pain as a natural part of life. Women, in particular, may downplay their pain to avoid burdening their families or communities. Understanding and addressing these cultural norms are crucial for developing effective pain management strategies.
Coping Strategies and Traditional Medicine
In the absence of accessible medical interventions, African women often turn to traditional healing practices to manage chronic pain. Herbal remedies, massage, and spiritual rituals are commonly employed. Integrating traditional medicine with evidence-based healthcare practices can provide a more comprehensive and culturally sensitive approach to chronic pain management.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in chronic pain management. However, there is a need for increased awareness and training among medical practitioners regarding the unique challenges faced by African women. Empathy, cultural competence, and a collaborative approach involving both traditional and modern medicine are essential elements of effective pain management strategies.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Empowering African women with chronic pain involves not only providing medical interventions but also offering education and support. Patient education programs can enhance awareness of pain management options, promote self-care practices, and reduce the stigma associated with seeking help for chronic pain.
Policy and Advocacy
Addressing chronic pain in African women requires a concerted effort at the policy level. Advocacy for improved healthcare infrastructure, increased access to pain management specialists, and the integration of pain management into primary healthcare services are critical steps toward alleviating the burden of chronic pain.
Conclusion
Chronic pain management in African women demands a holistic and culturally sensitive approach that acknowledges the unique challenges faced by this demographic. From addressing cultural attitudes toward pain to improving access to healthcare resources and fostering collaboration between traditional and modern medicine, there are myriad factors that must be considered. By adopting a comprehensive approach that encompasses medical, cultural, and socio-economic aspects, it is possible to enhance the well-being of African women living with chronic pain and pave the way for a healthier and more pain-aware society.